Page 98 - Catalogue Capteurs
P. 98
Fonctionnement, Solutions de détection de sécurité 0
encombrements, Interrupteurs de sécurité à levier ou à axe rotatif
raccordement En plastique à double isolation, à tête orientable,
types XCSPL, XCSTL, XCSPR et XCSTR
A entrée(s) de câble
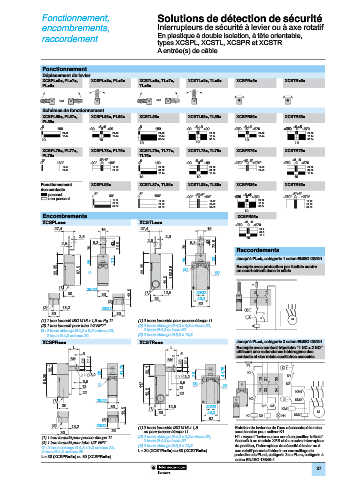
Fonctionnement
Déplacement du levier
XCSPLp9p, PLp7p, XCSPLp8p, PLp5p XCSTLp9p, TLp7p, XCSTLp8p, TLp5p XCSPRp5p XCSTRp5p
PLp6p TLp6p
ou ou
Schémas de fonctionnement
XCSPL59p, PL57p, XCSPL58p, PL55p XCSTL56p XCSTL58p, TL55p XCSPR55p XCSTR55p
PL56p
5˚ -5˚+5˚ 5˚ -5˚+5˚ -5˚+5˚ +5˚ +5˚
-5˚
-270˚
0 180˚ -90˚ 0 +90˚ 0 180˚ -90˚ 0 +90˚ -270˚ 0 +270˚ +270˚ 0 +270˚
21-22 21-22 21-22 21-22 21-22 21-22
13-14 13-14 13-14 13-14 13-14 13-14
10˚ 10˚ 33-34 33-34 10˚ 33-34
10˚ 10˚ 10˚
XCSPL79p, PL77p, XCSPL78p, PL75p XCSTL79p, TL77p, XCSTL78p, TL75p XCSPR75p XCSTR75p
PL76p TL76p
5° -5°+5° 5˚ -5˚ +5˚ +5° -5° +5˚ -5˚
0 180° -90° 0 +90° 0 180˚ -90˚ 0 +90˚ -270° 0 +270° -270˚ 0 +270˚
11-12 11-12 21-22 21-22 11-12 21-22
21-22 21-22 31-32 31-32 21-22 31-32
13-14 13-14 13-14
10˚ 10˚ 10˚
Fonctionnement XCSPL98p XCSTL87p, TL86p XCSTL88p, TL85p XCSPR85p XCSTR85p
des contacts
G passant 5° 5° -5°+5° +5˚ +5˚ -5°+5°
-5˚
0
H non passant 90° 0 180° -90° 0 +90° + -270˚270˚ 0 +270˚ -270° 0 +270°
11-12 11-12 11-12 21-22 11-12
21-22 21-22 21-22 13-14 21-22
31-32 31-32 31-32 33-34 31-32
10˚
Encombrements XCSPR95p
XCSPLppp XCSTLppp +5˚ -5˚
-270˚ 0 +270˚
27,4 16 27,4 16 21-22
31-32
2,5 2,5 10˚ 13-14
5,3 2,5 5,3 43
2,5 43 72,5 72,5
70 70
Raccordements
28 33 28 33 Jusqu’à PL=b, catégorie 1 selon EN/ISO 13849-1
23,35 87,5 23,35 108,35 (3) (2) Exemple avec protection par fusible contre
un court-circuit dans le câble
12,5
(1) 20/22 F1
30 30 13,5 (1) 12,5 20/22 21 13
30 40,3
(2) 52 22 14
(2) 13,2 20/22 O
30 30
I X
(1) 1 trou taraudé ISO M16 x 1,5 ou Pg 11 (1) 2 trous taraudés pour presse-étoupe 11 M
(2) 1 trou taraudé pour tube 1/2 NPT” (2) 2 trous oblongs Ø 4,3 x 8,3 entraxe 22, X
Ø : 2 trous oblongs Ø 4,3 x 8,3 entraxe 22, 2 trous Ø 4,3 entraxe 20
2 trous Ø 4,3 entraxe 20 (3) 2 trous oblongs Ø 5,3 x 13,3
XCSPRppp XCSTRppp Jusqu’à PL=d, catégorie 3 selon EN/ISO 13849-1
L L Exemple avec contact tripolaire “1 NC + 2 NO”
5 5 utilisant une redondance hétérogène des
M4 M4 contacts et des relais auxiliaires associés
32,1 28 41,75 32,1 41,75 F1 O
K1
96,25 8,5 3,2 8,5 3,2 28 13 21 33 K1
13 117 13 (3) (2) K2
22 12,5 22 14 22 34 KM1
(1) 20/22 K2 I KM2
30 30 (1) 12,5 20/22 K1 K2 KM1
13,5 30 40,3 KM2 M
(2) 52 K1 K2 H1
(2) 13,2 20/22 (1) 2 trous taraudés ISO M16 x 1,5 Rotation du levier ou de l’axe nécessaire à la mise
30 30 ou pour presse-étoupe 11 sous tension pour activer K1.
(1) 1 trou taraudé pour presse-étoupe 11 (2) 2 trous oblongs Ø 4,3 x 8,3 entraxe 22, H1 : voyant “levier ou axe non à sa position initiale”.
(2) 1 trou taraudé pour tube 1/2” NPT 2 trous Ø 4,3 entraxe 20 Associé à un module XPS et à un autre interrupteur
Ø : 2 trous oblongs Ø 4,3 x 8,3 entraxe 22, (3) 2 trous oblongs Ø 5,3 x 13,3 de position, l’interrupteur de sécurité à levier ou à
2 trous Ø 4,3 entraxe 20 L = 30 (XCSTRp5p) ou 80 (XCSTRp6p) axe rotatif permet d’obtenir un verrouillage de
L = 30 (XCSPRp5p) ou 80 (XCSPRp6p) protection de PL=d, catégorie 3 ou PL=e, catégorie 4
selon EN/ISO 13849-1.
37